Harnessing the power of T cells to fight infection
Transforming human T cell responses into effective vaccines for infectious disease and cancer.
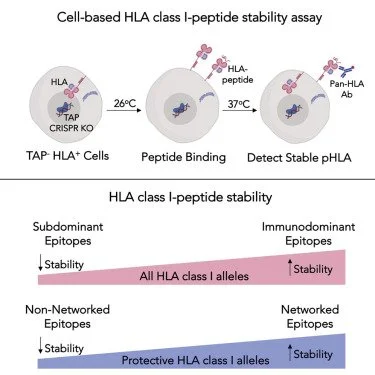
The Gaiha Lab is working to establish a T cell vaccine platform that incorporates target epitope identification, HLA-epitope stability assessments, T cell immunogen design, viral vector production, and iterative testing in small animal models. We work with a structure-based network analysis technology, which integrates network theory with protein structure data to define topologically important and mutationally constrained regions of viral proteins. We utilized this approach to identify key targets of CD8+ T cells in individuals who spontaneously control HIV (Gaiha et al., Science 2019) and, more recently, identify mutation-resistant epitopes in SARS-CoV-2 (Nathan, Rossin, et al., 2021). The overarching goal is to integrate these technologies towards developing prophylactic and therapeutic vaccines for HIV, SARS-CoV-2, and HPV and ultimately for broad translation to infectious diseases and cancer.